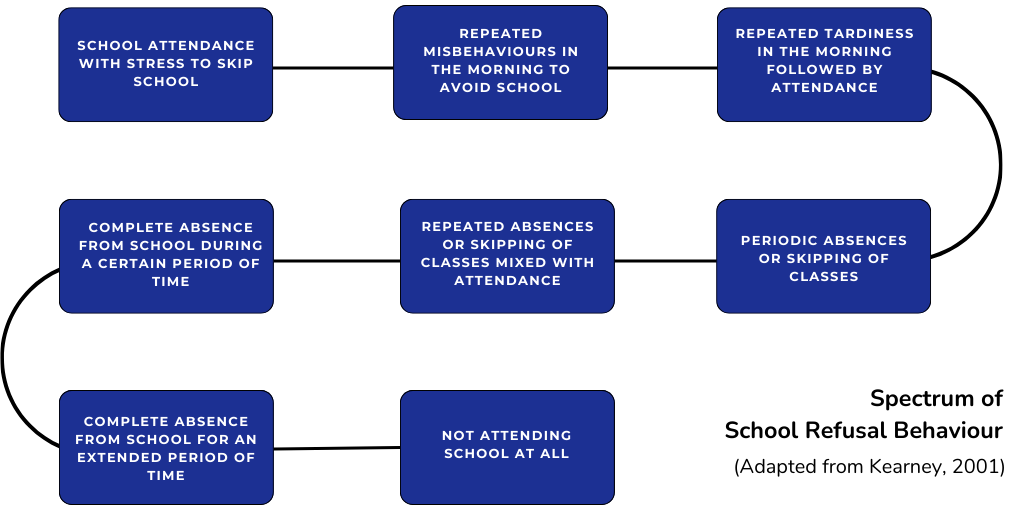
Overcoming Anxiety and School Refusal: Strategies for Success
Social anxiety is a common concern for children and adolescents, characterized by a persistent and excessive fear of social situations. Learn how to prevent anxiety from turning into school refusal.